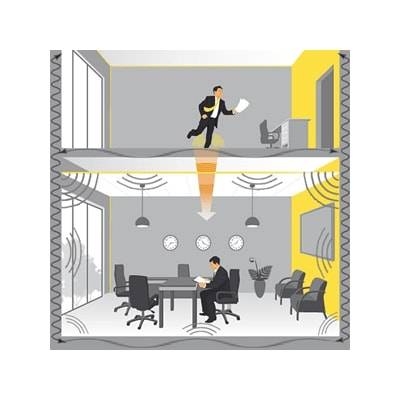
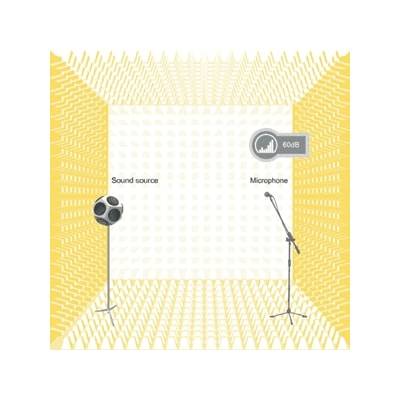
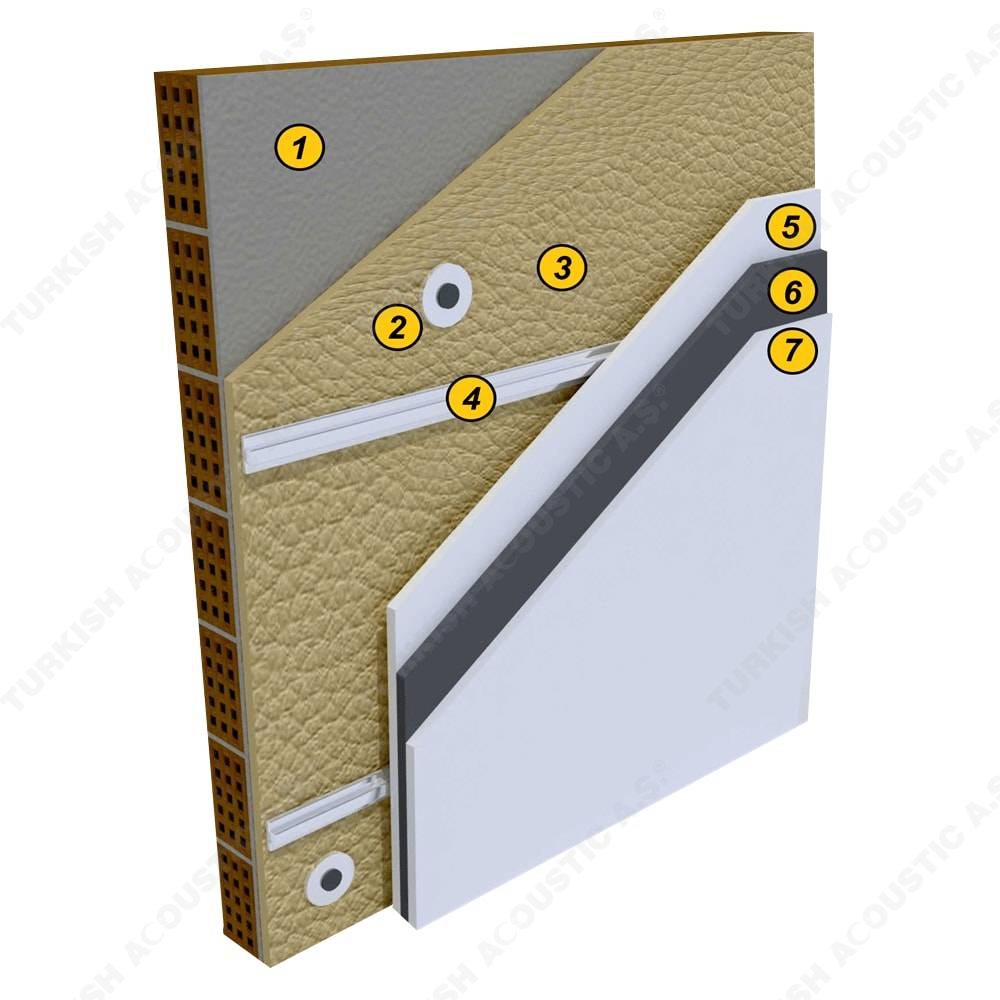
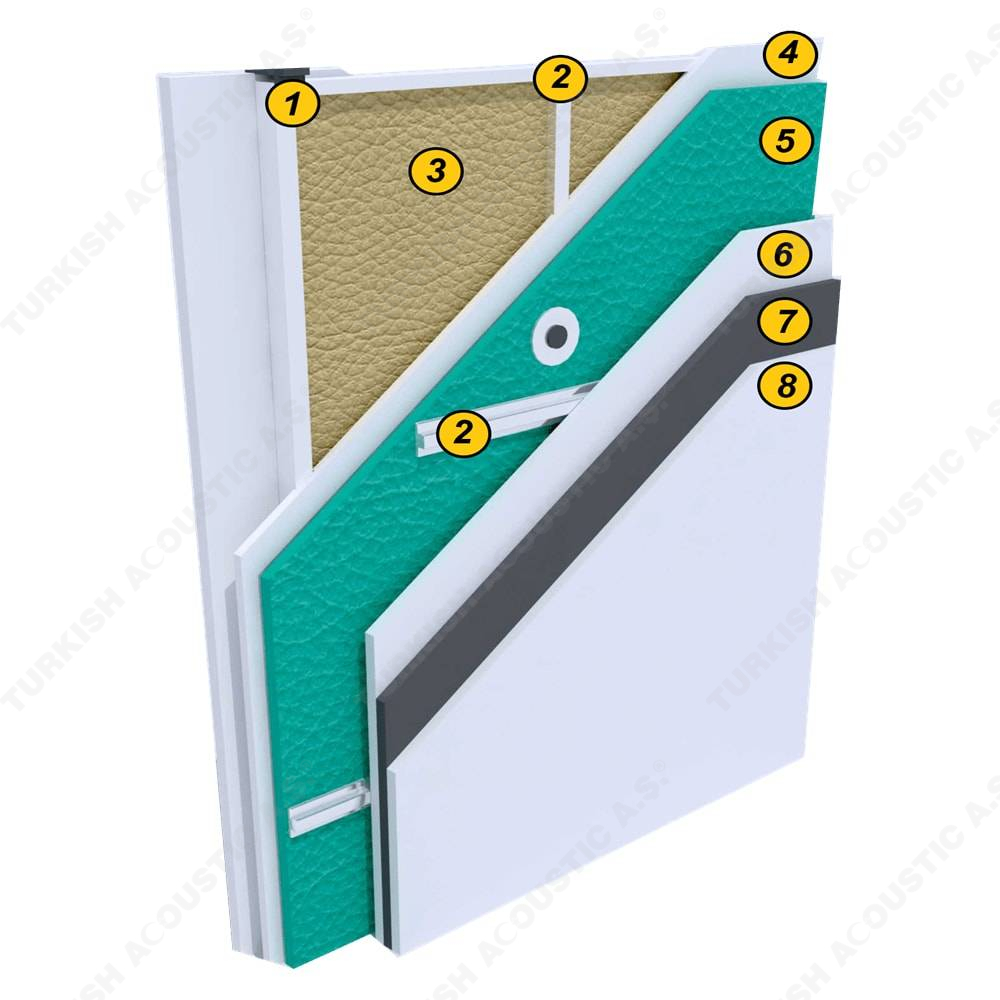
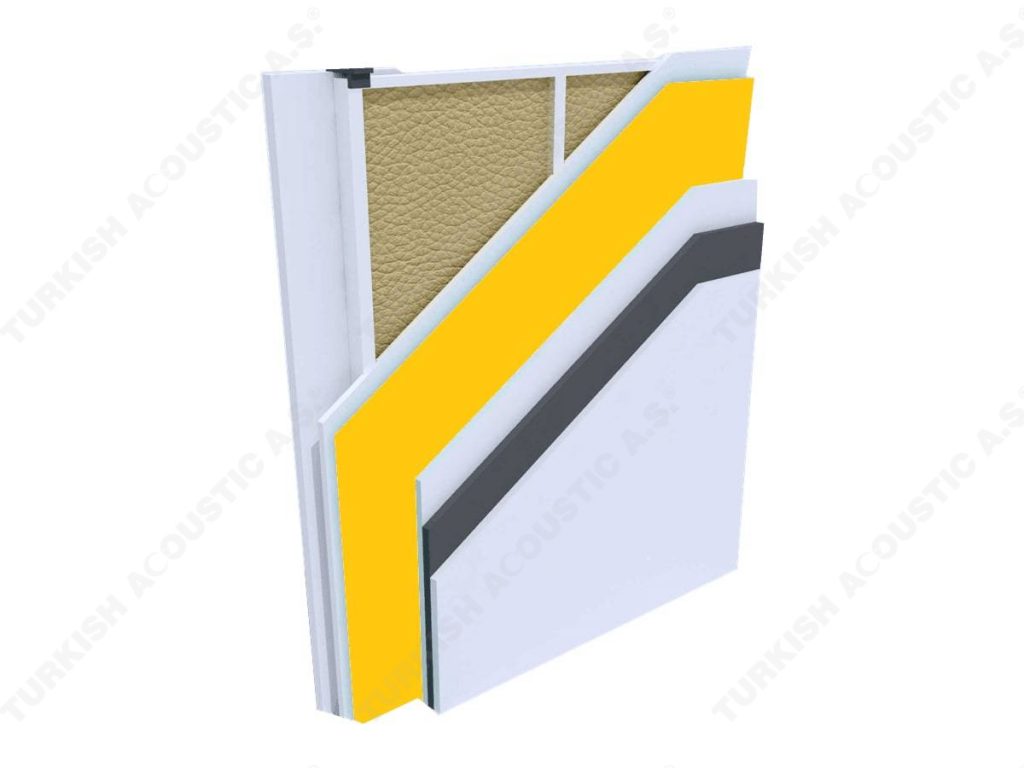
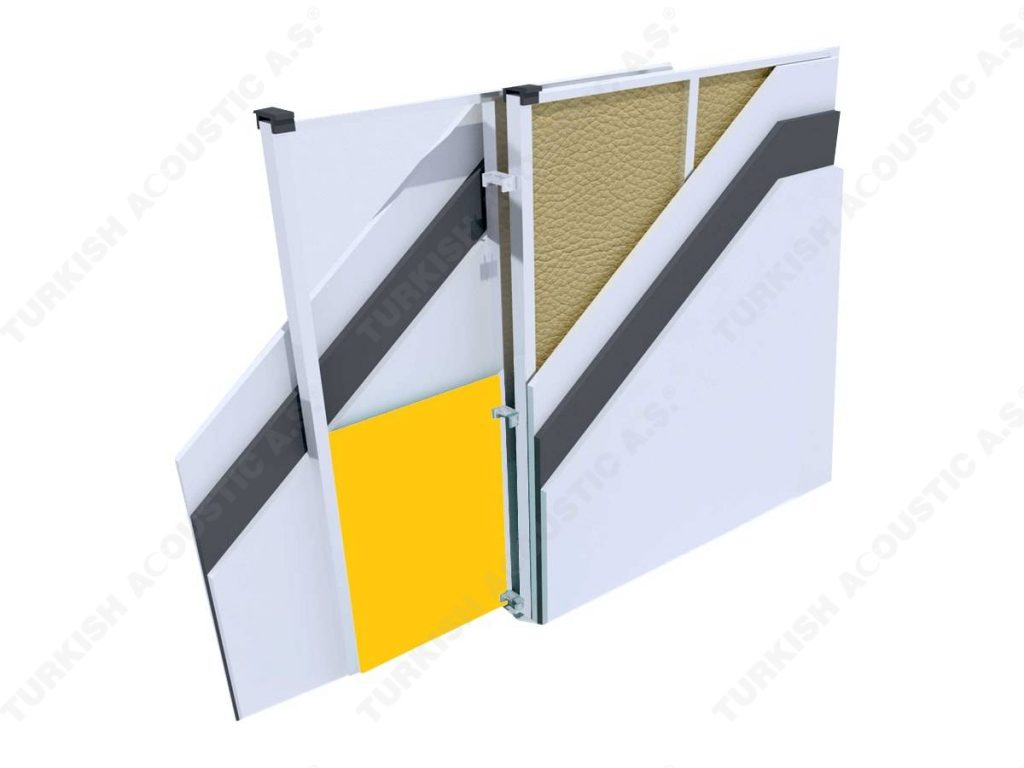
What is Sound Insulation?: Sound insulation means isolating the sound in the environment with sound insulation materials. It is the best and the most efficient solution to protect ourselves from the unwanted sounds and noises in our daily life. With sound insulation, it is possible to prevent the sound waves from passing from one place to another and to reduce the noise at its point of source. Sound insulation problems usually occur in places such as houses, meeting rooms, generator rooms, machine rooms, schools, libraries, and call centers.
1. Sound Insulation
The system intended for sound insulation includes the measurements to minimize the damage caused by the noise on the human. Any sound, that is incompatible, irregular, and disturbing is called noise.
1.1 Preventing the Damages of the Sound: Noise pollution is one of the problems that are harmful to human health and life comfort in cities that have unplanned urbanization. Sounds and noises coming from factories, airports, traffic, and our neighbors are disturbing and harmful to our health.
1.2 Sound: Beams that move through air particles are matters. Two different methods are used for preventing unwanted sound waves and noise. Acoustic regulations and sound insulation. Acoustic regulations are applied to regulate the reverberation time indoors, that is to say, to decrease the intensity of sound by absorbing the sound waves at their source. Sound insulation is applied for providing the transient loss of the sound from one place to another with sound isolation products.
2. Advantages of Sound Insulation
2.1. Sound Insulation Provides Healthy and Comfortable Environments: Noise is an unwanted and disturbing factor for our comfort and, living in an environment without noise pollution is not a luxury but a requirement. This factor causes psychological and physiological disturbances as well as negative issues in terms of performance.
30-65 dBA I. 1st Grade Noises
- Discomfort
- Disturbance
- Feeling bored
- Anger
- Loss of Concentration
- Sleep Disorder
65-90 dBA II. 2nd Grade Noises
- Physiological Noise
- Changes in Heartbeat
- Accelerated Breathing
- Decreased Pressure in the Brain
90-120 dBA III. 3rd Grade Noises
- Physiological Noise
- Headache
120-140 dBA IV. 4th Grade Noises
- Physiological Noise
- Headache
140 dBA V. 5th Grade Noises
2.2. Sound Insulation Makes People Efficient
Because of the disturbance caused by the noise, the performance of the workers who work in industrial places like factories decreases, and as a result of that, distractibility and occupational accidents happen. The decrease in performance affects the establishments economically. A similar effect can also be seen with students. Students exposed to noise are distracted, and their concentration is disturbed, so they move away from the lesson and cannot perceive the given information healthily and efficiently. It has been proven by research that aircraft noise reduces long-term remembering and perception skills. To set an example as a result of the researches which has been carried out on inhabitants who live around Munich Airport, it has been proven that the noise is harmful to human health. Humans must be isolated from noise with sound insulation to continue their life efficiently.
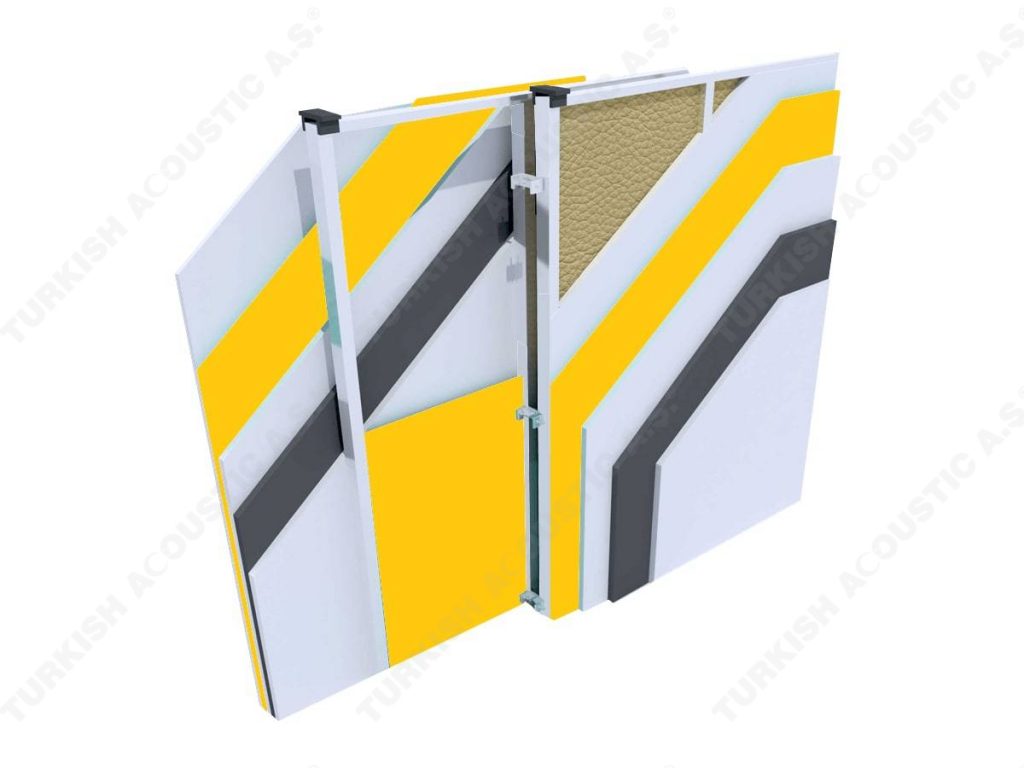
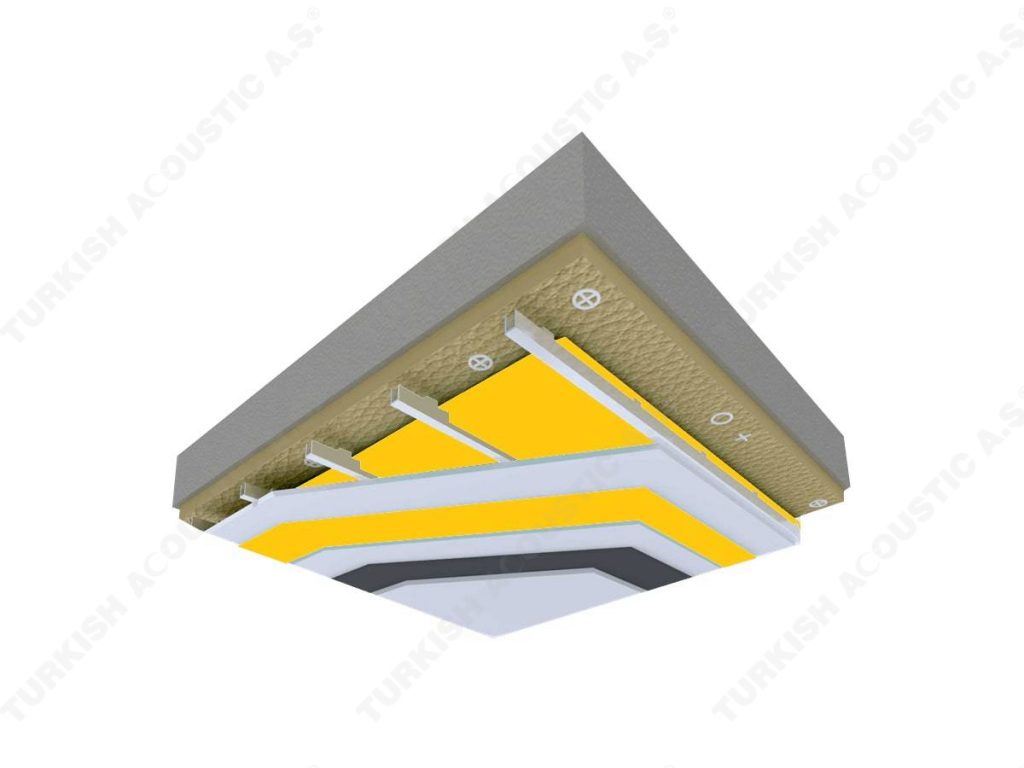
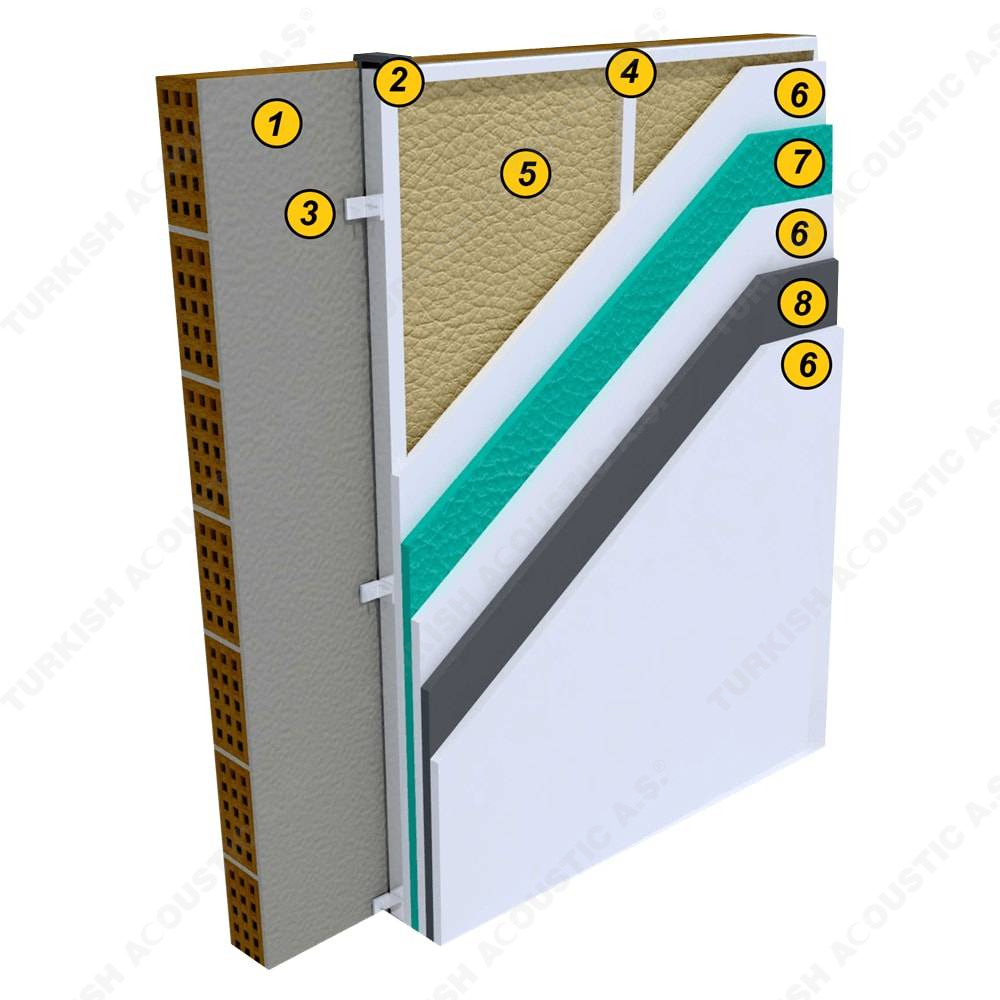
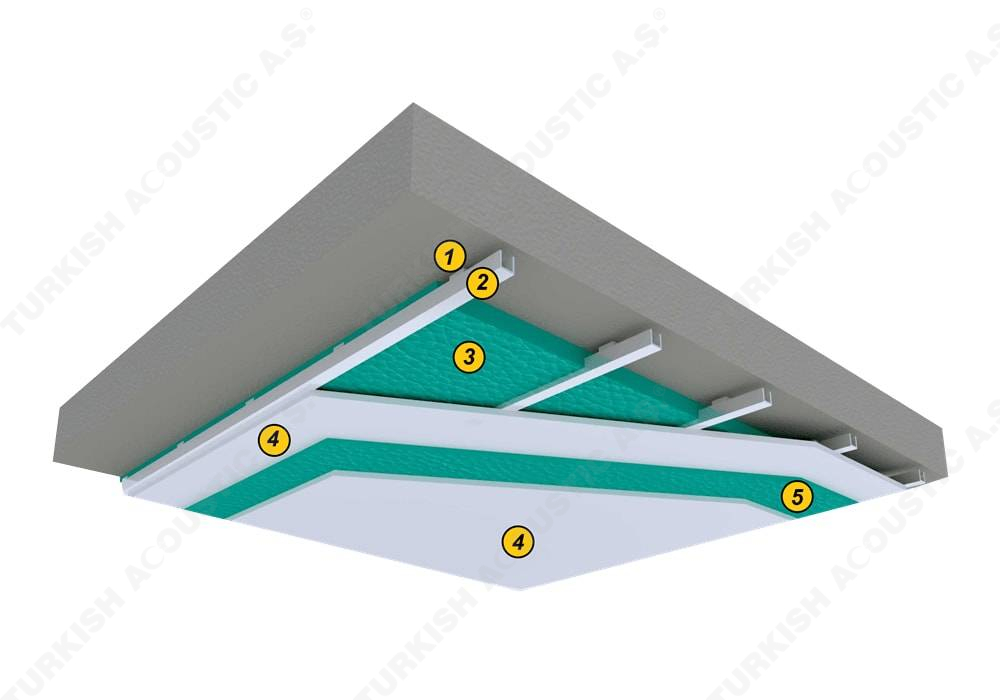
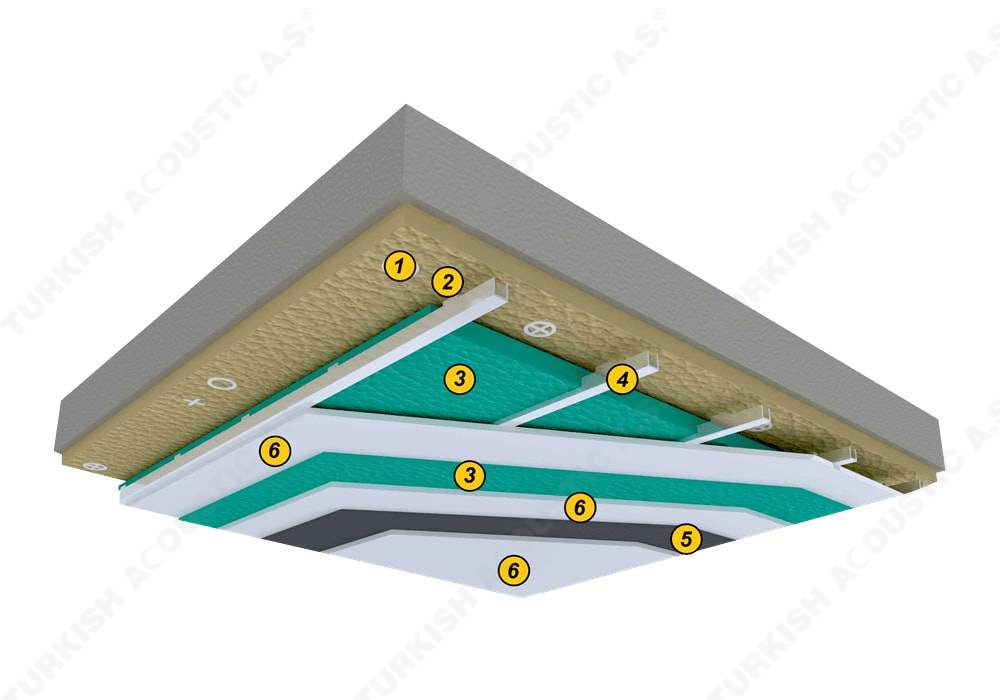
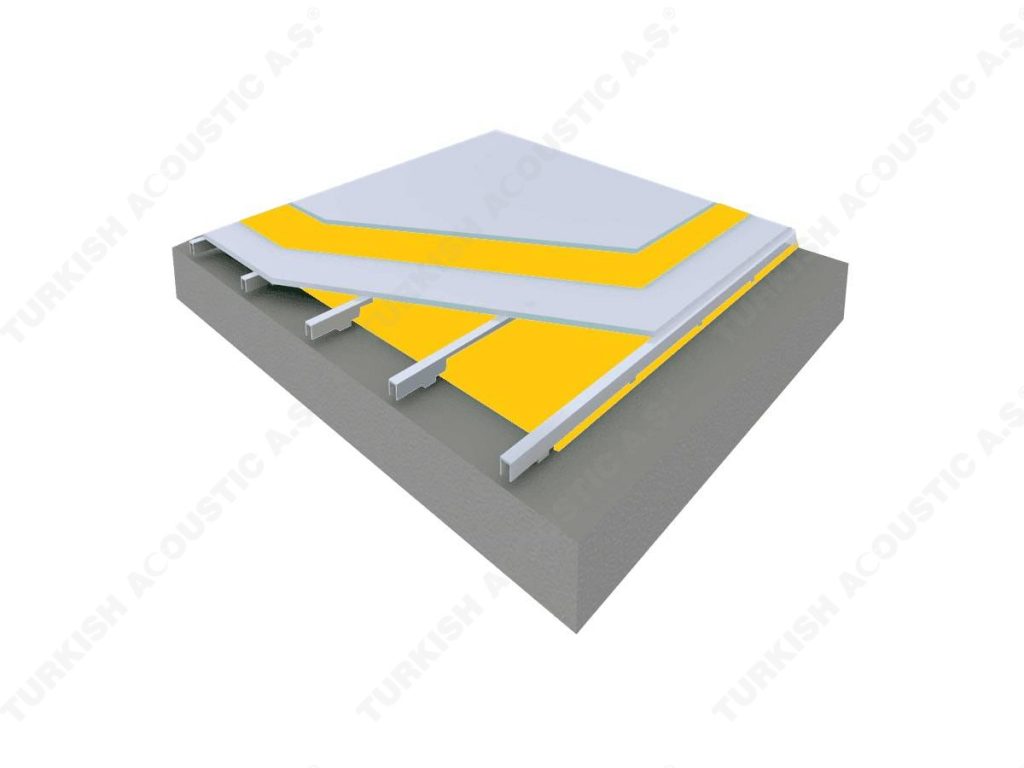
3. SOUND INSULATION MATERIALS
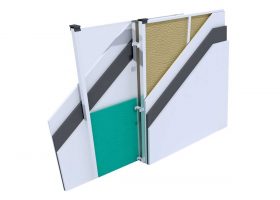
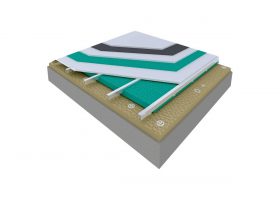
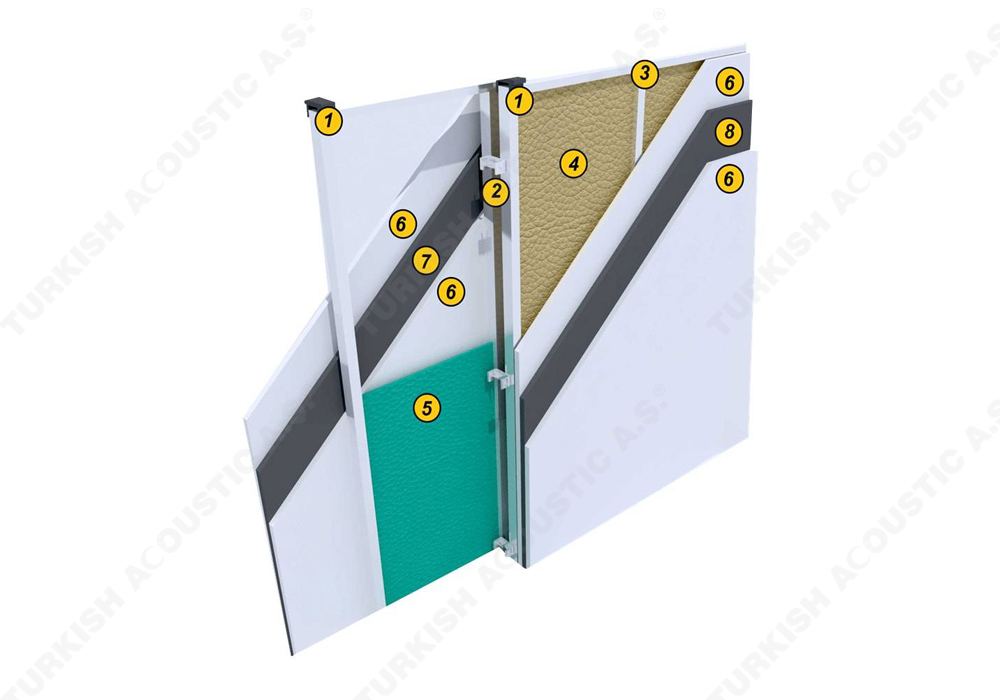
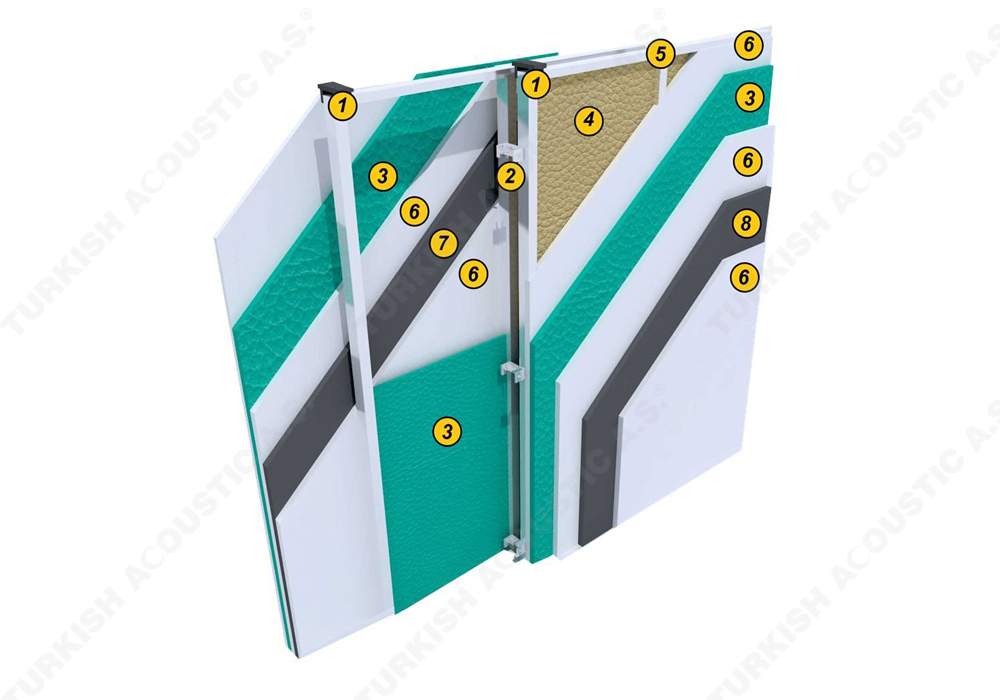
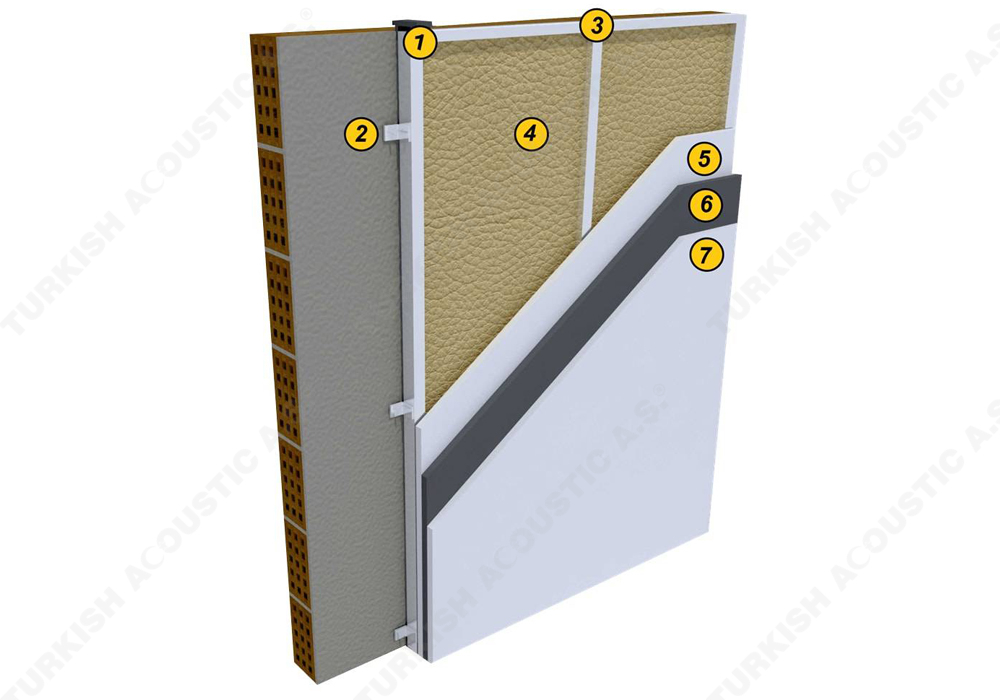
I. Building Insulation
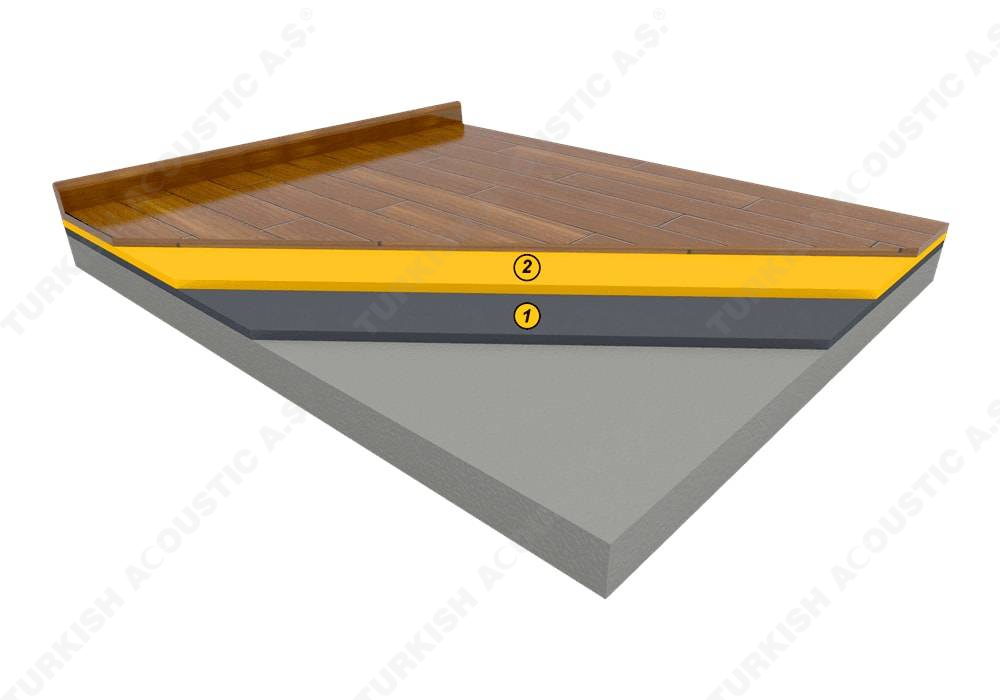
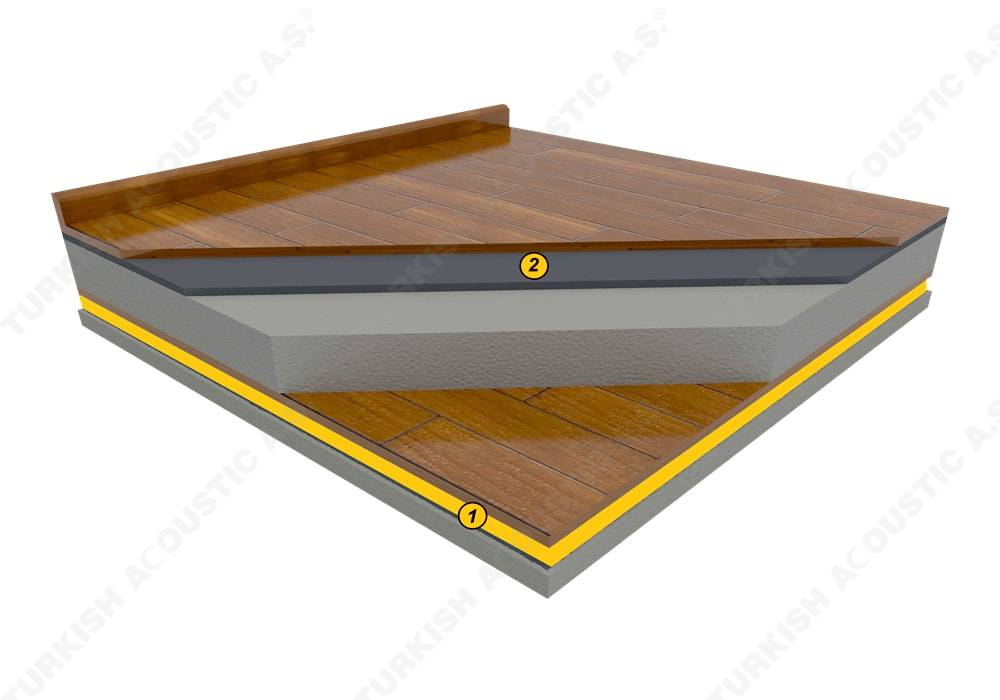
Wall, Floor, Roof Applications: Acoustic sponges, rubber barriers, soft polyurethane based sponges, melamine sponge, felt, perforated metals, perforated woods, perforated gypsum panels, cork. Flooring Applications (to prevent only the impact sound): Polyethylene, rubber foam, merchandise materials made of textile waste.
II. Insulating Glass Units Acoustic Laminated Glass Solutions
III. Technical (Industrial) Insulation Acoustic sponge, acoustic products, acoustic mattresses, polyethylene, polyurethane, rubber foam, suspension equipment, hangers, sound absorbers, etc.
4 . STANDARDS AND LEGISLATION REGARDING SOUND INSULATION IN APPLICATION
- TS 901 (01.11.1972): Fibrous Heat and Sound Insulation Material
- TS EN ISO 140-1 (18.03.2002): Acoustic - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and Building Elements - Part 1: Suppressed Rules for Side Conduction Laboratory Test Sites
- TS EN ISO 140-3 (16.01.1996): Acoustics - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Structures and Building Elements - Part 3: Measurement of Airborne Sound Insulation Value of Building Elements
- TS ISO 140-4 (16.01.1996): Acoustics - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and Building Elements - Part 4: Field Measurements of Airborne Sound Insulation Between Rooms
- TS ISO 140-5 (16.01.1996): Measurement of Sound Insulation in Acoustic Structures and Building Elements - Part 5: Field Measurements of Air Diffused Sound Insulation of Exterior Wall Cladding Elements and Exterior Cladding
- TS EN ISO 140-6 (18.03.2002): Acoustics - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and Building Elements - Part 6: Laboratory Measurements of Impact Sound Insulation of Soils
- TS EN ISO 140-12 (01.04.2002): Acoustic - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and Building Elements - Part 12: Air and Air in an Accessible Ground Floor Laboratory Measurements of Sound Insulation Between Rooms by Impact.
- TS EN 20140-2 (16.01.1996): Akustik – Acoustic - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and Building Elements - Part 2: Determination, Verification and Application of Precision Information
- TS EN 20140-9 (16.01.1996): Acoustics - Measurement of sound insulation in buildings and building elements Part 9: Top Completed with a filler in the room from the room in a suspended ceiling air processing Emitted Soundproofing of laboratory measurements
- TS EN 20140-10 (16.01.1996): Acoustics - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Structures and Building Elements - Part 10: Laboratory Measurements of Airborne Sound Insulation in Small Building Elements
- TS EN 12758 (11.11.2002): Glass - Glass Systems Used in Buildings and Airborne Sound Insulation - Characteristics and Determinations
4.1. Current rules regarding sound insulation
4.1. Current rules regarding sound insulation
- TS 2381 (05.04.1976): Assessment of Sound Insulation in Residences
- “Regulation on Assessment and Management of Environmental Noise 2002/49” published in the official gazette 01 July 2005 dated and 25862 numbered.
- “Regulation on Health and Safety in Construction Works” published in the official gazette 23 December 2003 dated and 25325 numbered.
- “Noise Regulation” published in the official gazette 23 December 2003 dated and 25325 numbered.
- “Vibration Regulation” published in the official gazette 23 December 2003 dated and 25325 numbered.
- “Regulation on Health and Safety Conditions in the Use of Work Equipment” published in the official gazette 11 February 2004 dated and 25370 numbered.
- “Regulation on the Use of Personal Protective Equipment in Workplaces” published in the official gazette 11 February 2004 dated and 25370 numbered.
- “Regulation on the Procedures and Principles of Employees” published in the official gazette 07 April 2004 dated and 25426 numbered.